acl vs pcl tear drawer test|partial tear of pcl : distribute PCL injuries are traumatic knee injuries that may lead to posterior knee instability and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (i.e PLC, ACL). Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with a . The F0 cycle is based on the concept of thermal equivalence, where the F 0 value represents the equivalent minutes of sterilization at 121.1°C. For instance, a sterilization cycle with a F 0 of 3 indicates a process equivalent to .
{plog:ftitle_list}
El uso de vacío y presión permite inyectar tratamientos profundamente en el núcleo de la Madera de Pino, de la manera más eficiente. Dependiendo de la situación y el tipo de .
what is a pcl rupture
Results from a blinded, randomized, controlled study shows that the accuracy for detection of a PCL-tear is 96%, with 90% sensitivity and a 99% specificity. For grade 2 and grade 3 posterior laxity, the examination accuracy was higher than for grade 1 posterior laxity.Other recent research has identified the anterior drawer test as a more effective . PCL injuries are traumatic knee injuries that may lead to posterior knee instability and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (i.e PLC, ACL). Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with a .
Results from a blinded, randomized, controlled study shows that the accuracy for detection of a PCL-tear is 96%, with 90% sensitivity and a 99% specificity. For grade 2 and grade 3 posterior laxity, the examination accuracy was higher than for grade 1 posterior laxity.
PCL injuries are traumatic knee injuries that may lead to posterior knee instability and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (i.e PLC, ACL). Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with a traumatic knee effusion and increased laxity on a posterior drawer test but requires an MRI for confirmation.
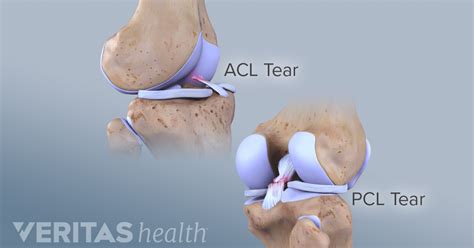
Other recent research has identified the anterior drawer test as a more effective test to identify chronic conditions, with a sensitivity and specificity of 0.92 and 0.91. The laxity of the ACL or the instability of the knee depends on the forces applied to the knee and increases with higher force. The ACL and PCL are two major ligaments that crisscross within the joint, allowing the knee to flex and extend without sliding back and forth. The ACL prevents the tibia from sliding forward along the femur, while the PCL prevents the tibia and femur from sliding backwards. ACL tears are common athletic injuries leading to anterior and lateral rotatory instability of the knee. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with presence of a traumatic knee effusion with increased laxity on Lachman's test but requires MRI studies to confirm diagnosis.
Anterior Drawer Test (ACL): Similar to the Lachman test, the anterior drawer test assesses anterior tibial displacement with the knee flexed at 90 degrees. Increased anterior translation can indicate ACL injury. Posterior Drawer Test (PCL): For PCL evaluation, the posterior drawer test is performed. In this test, the knee is flexed at 90 .
What is the difference between an anterior drawer test and a Lachman test? The anterior drawer test and the Lachman test are both physical movement tests that help healthcare providers diagnose ACL tears. A Lachman test is a variation of the anterior drawer test. Healthcare provider often perform a posterior drawer test to assess the function of the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)—one of the four ligaments of the knee. If your healthcare provider suspects a PCL tear, the posterior drawer test is the best test to diagnose it.
The posterior drawer test: This is the most accurate test for assessing PCL integrity. It is performed with the patient in a supine position with the hip flexed to 45 degrees and knee flexed to 90 degrees. A posterior force is applied to the proximal tibia whilst the femur is stabilized. anterior cruciate ligament. ( ACL. ), posterior cruciate ligament. ( PCL. ), medial collateral ligament. ( MCL. ), and. lateral collateral ligament. ( LCL. ) result in knee pain and instability. Various maneuvers can be used to evaluate the stability of the joint and usually suffice to diagnose collateral. ligament. tears. An. MRI. is the best.Results from a blinded, randomized, controlled study shows that the accuracy for detection of a PCL-tear is 96%, with 90% sensitivity and a 99% specificity. For grade 2 and grade 3 posterior laxity, the examination accuracy was higher than for grade 1 posterior laxity. PCL injuries are traumatic knee injuries that may lead to posterior knee instability and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (i.e PLC, ACL). Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with a traumatic knee effusion and increased laxity on a posterior drawer test but requires an MRI for confirmation.
Other recent research has identified the anterior drawer test as a more effective test to identify chronic conditions, with a sensitivity and specificity of 0.92 and 0.91. The laxity of the ACL or the instability of the knee depends on the forces applied to the knee and increases with higher force. The ACL and PCL are two major ligaments that crisscross within the joint, allowing the knee to flex and extend without sliding back and forth. The ACL prevents the tibia from sliding forward along the femur, while the PCL prevents the tibia and femur from sliding backwards.
sprained pcl recovery time
ACL tears are common athletic injuries leading to anterior and lateral rotatory instability of the knee. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with presence of a traumatic knee effusion with increased laxity on Lachman's test but requires MRI studies to confirm diagnosis. Anterior Drawer Test (ACL): Similar to the Lachman test, the anterior drawer test assesses anterior tibial displacement with the knee flexed at 90 degrees. Increased anterior translation can indicate ACL injury. Posterior Drawer Test (PCL): For PCL evaluation, the posterior drawer test is performed. In this test, the knee is flexed at 90 . What is the difference between an anterior drawer test and a Lachman test? The anterior drawer test and the Lachman test are both physical movement tests that help healthcare providers diagnose ACL tears. A Lachman test is a variation of the anterior drawer test. Healthcare provider often perform a posterior drawer test to assess the function of the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)—one of the four ligaments of the knee. If your healthcare provider suspects a PCL tear, the posterior drawer test is the best test to diagnose it.
The posterior drawer test: This is the most accurate test for assessing PCL integrity. It is performed with the patient in a supine position with the hip flexed to 45 degrees and knee flexed to 90 degrees. A posterior force is applied to the proximal tibia whilst the femur is stabilized.

Here's a simplified guide to incorporating Speed-Clean into your autoclave maintenance routine: A) With a cooled chamber, drain the reservoir and fill it with clean water. B) Add one ounce of Speed-Clean sterilizer .
acl vs pcl tear drawer test|partial tear of pcl